LENGKAP Pengertian Ius Soli dan Ius Sanguinis Contoh dan Perbedaan

The Statutes at Large; being a Collection of all the Laws of Virginia from the First Session of the Legislature, in the year 1619. By William Waller Hening, Vol. X (1822), Ch. LV, p. 129. Nationality: Jus Soli or Jus Sanguinis - Volume 24 Issue 1.
Jus Sanguinis 1 HUGE GUIDE Italian Citizenship by Descent

The 1867 civil code additions also softened the jus sanguinis requirements of the 1826 charter by allowing for jus sanguinis by declaration of desire for Portuguese nationality as an alternative to actual residence in Portugal. Naturalisation was extended automatically to a foreign woman who married a Portuguese man. The 1867 code also updated.
From Jus Soli to Jus Sanguinis A Historical Analysis of the Evolution of Philippine Citizenship

In states in which the jus sanguinis principle applies (i.e. France and Germany), a conflict of jurisdiction may arise when a child is born of parents who are citizens of another state. For example, a child born in the United States of French parents is an American citizen jure soli, but a French citizen jure sanguinis.
Difference Between Jus Soli and Jus Sanguinis EuroPassport Inc. Blog

Jus soli (English: / dʒ ʌ s ˈ s oʊ l aɪ / juss SOH-ly [citation needed], / j uː s ˈ s oʊ l i / yooss SOH-lee), meaning 'right of the soil', is the right of anyone born in the territory of a state to nationality or citizenship, also commonly referred to as birthright citizenship in some Anglophone countries, is a rule defining a person's nationality based on their birth in the territory.
What is jus soli? Definition and example Market Business News

NATIONALITY: tJUS SOLI" OR "JUS SANGUINIS"' 61. an able Chief Justice of the United States, the other by the Dictator of. Europe. The Williams Case (Wharton's State Trials, 652), decided in 1799 by Chief Justice Ellsworth, in the Circuit Court of the United States, was one of. citizenship.
Cidadania "Jus Sanguinis" x "Jus Solis" YouTube

3. Birthright citizenship is a New World philosophy. As University of California, San Diego sociologist John Skrentny told NPR in 2010, the U.S. is an anomaly in the world when it comes to this.
What Offers Citizenship Land or Blood? Rule of the Land Rule of the Blood ymbia Jus Soli
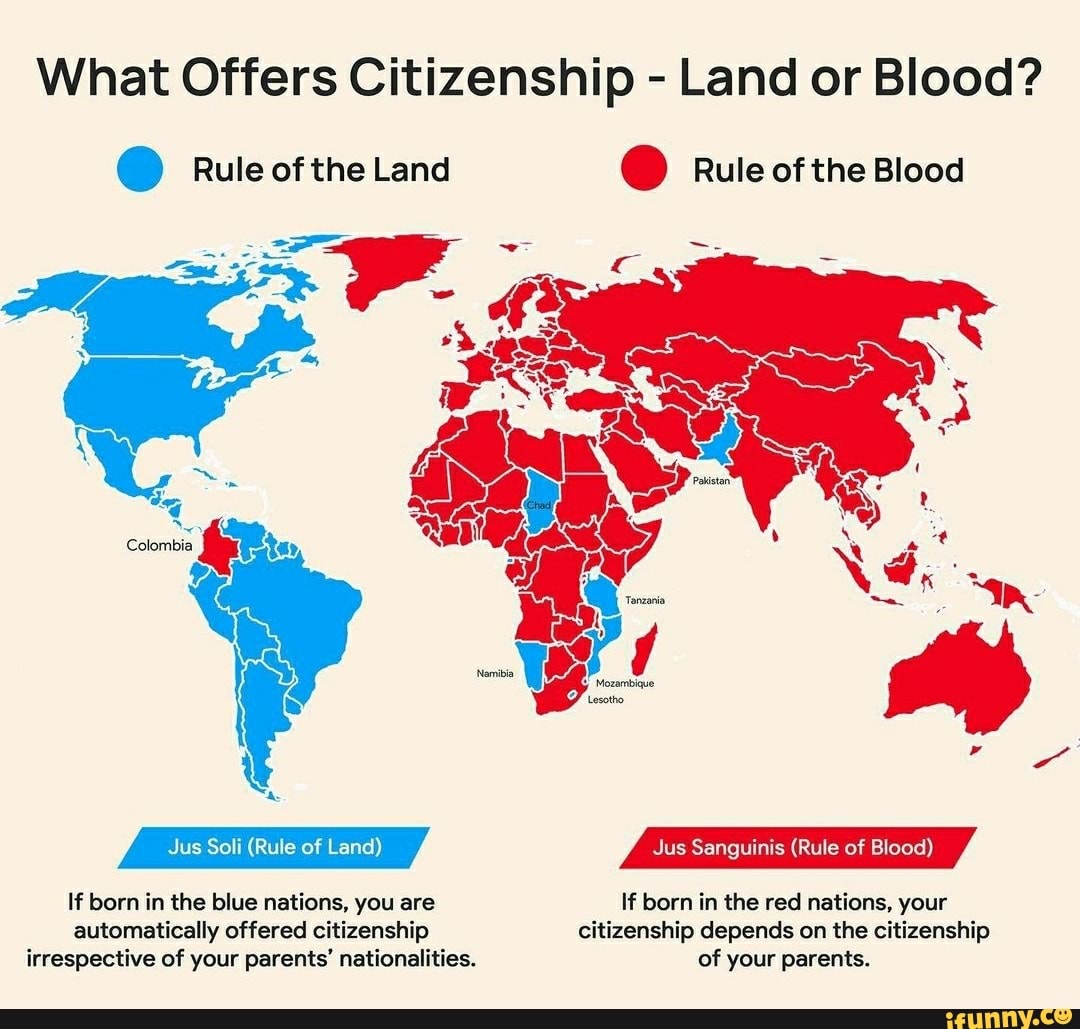
jus soli, in legal theory, the rule or law that provides that citizenship is acquired by birth within the territory of the state, regardless of parental citizenship. Originating in English common law, jus soli serves as the basis for citizenship in nearly every nation-state in the Western Hemisphere and as the foundation for the Fourteenth Amendment to the Constitution of the United States.
JUS SOLI VS JUS SANGUINIS

soil: jus sanguinis; jus soli. Moreover, through this juridical regime, the factual accidents of "blood" and "soil" combine to miraculously con-stitute a citizenry—and a noncitizenry—both uniquely available to beneWt capital.5 SMall WondeR: It'S no MIRaCle "Despite an abundance of awful wretchedness," the BFI monograph
Jus Soli and Jus Sanguinis The Law Firm of Talampas & Associates

Philippines - Effect Of Jus Soli And Jus Sanguine. January 15, 2021 by Conventus Law. About a year ago, the House of Representatives conducted hearings on the franchise renewal of a media company and brought to the fore the concept of 'dual citizenship'. The Chairman of the company happens to be both an American and a Filipino citizen.
PPT Jus Sanguinis and Jus Soli Citizenship Rights PowerPoint Presentation ID9642015

In the U.S., children obtain their citizenship at birth through the legal principle of jus soli ("right of the soil")—that is, being born on U.S. soil—or jus sanguinis ("right of blood.
PPT Jus Sanguinis and Jus Soli Citizenship Rights PowerPoint Presentation ID9642015

The jus sanguinis citizenship statute, although modified several times, remained silent on the question of nonmarital children's citizenship 21 until 1940, when Congress codified a modernized version of the Guyer rule by continuing the default exclusion of nonmarital foreign-born children of American fathers. 22 Part III tells the story of.
What is jus sanguinis? Definition and examples Market Business News

Birthright citizenship refers to the legal status of citizenship when acquired through birth to a citizen parent ( ius sanguinis) or birth in the territory of a state ( ius soli ). This is how most people acquire citizenship, often unconditionally and automatically at birth. A minority across the globe acquire citizenship through naturalization.
PPT Jus Sanguinis and Jus Soli Citizenship Rights PowerPoint Presentation ID9642015

The author wishes to acknowledge the Australian European University Institute Fellowships Association Inc. for the award of a six-month Postdoctoral Fellowship at the European University Institute in 2015 that made it possible to pursue the research project: 'From jus sanguinis to jus soli: Representing Somalis' Multiple Affiliations.'I am grateful to Professor Anna Triandafyllidou.
What Are The Differences Between Jus Sanguinis and Jus Soli? YouTube

jus soli. [Latin: law relating to the soil (of one's country)]The rule by which birth in a state is sufficient to confer nationality, irrespective of the nationality of one's parents (compare jus sanguinis). The United Kingdom and the United States originally adhered to a strict version of this principle. Thus the children of an alien, born on.
How to Acquire an AUSTRALIAN CITIZENSHIP Jus Soli and Jus Sanguinis in Australia AUSSIE LAW

Jus Sanguinis, used interchangeably with Jure sanguinis, are Latin words that mean "by right/virtue of blood", its literal translation, "blood right.". At present, Italy predominantly grants recognition of citizenship through jus sanguinis. In respect of the principle of jus soli, only in rare and exceptional circumstances does Italian.
Documents Required for Italian Citizenship by Descent (Jure Sanguinis / Jus Soli & 1948 Case

As you may know the terms jus soli and jus sanguinis derive from Latin and are used in citizenship law. More specifically, jus soli means "right of soil"; under this system, the right of citizenship is acquired by being born in a country, regardless of the nationality of an individual's parents. There are more than 30 countries in the.
.